Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (9): 1319-1324.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.09.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation methods for small vascular network distribution and counting around the knee joint in rats
Wang Le, Lou Ai-ju, Ding Qiang, Yang Bo, Chen Tao, Tang Long, Zhang Bo, Yin Biao, Song Ting, Zhang Zhi
- Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2014-02-26Published:2014-02-26 -
Contact:Zhang Zhi, Master, Chief physician, Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wang Le, Master, Attending physician, Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31200726; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. s2013010011532; the Science and Technology Plan of Guangzhou City, No. 2013J4100101
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Le, Lou Ai-ju, Ding Qiang, Yang Bo, Chen Tao, Tang Long, Zhang Bo, Yin Biao, Song Ting, Zhang Zhi. Evaluation methods for small vascular network distribution and counting around the knee joint in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(9): 1319-1324.
share this article
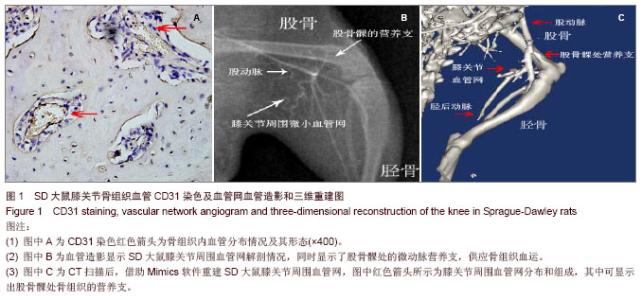
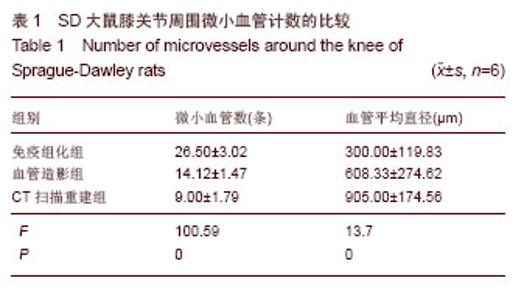
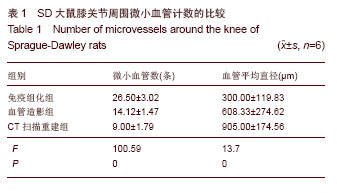
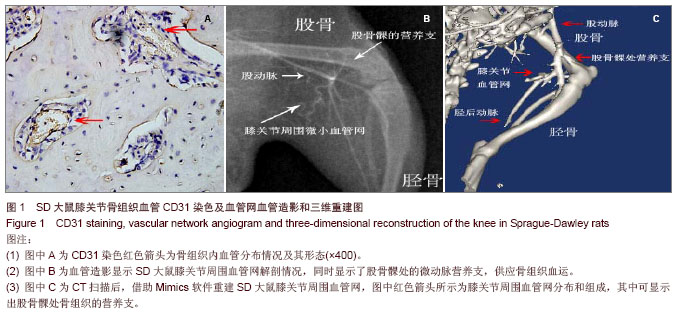
2.1 SD大鼠膝关节周围微小动脉网的分布情况 免疫组化染色后可见膝关节周围有较丰富的微小血管分布,主要营养周围肌肉组织,小动脉形态清晰(图1A),部分微动脉与微静脉的辨认较困难。 血管造影摄片后可以显示SD大鼠膝关节周围血管网的分布整体情况,可见膝关节周围血管网主要起于股动脉,在膝关节上方约股骨髁水平的内后方分为数支小动脉,营养膝关节周围的肌肉组织(图1B),并有一二支细小分支进入股骨远端或胫骨平台,营养该处骨组织,但该分支在不同大鼠间存在变异。在摄片组中,显影检测出该分支的大鼠有3只,占50%。膝关节周围血管网中最大的一支血管在小腿后方的肌肉组织中延续下行,移行为胫后动脉,主要营养下肢的肌肉和骨组织。 2.2 SD大鼠膝关节周围微血管计数 在免疫组化检测组中,膝关节横断面切片中可见褐色深染的部位,考虑为微血管所在的位置(图1A),在×400镜下可见管状样微血管结构,根据软件计算,膝关节周围微血管网分支为(26.50±3.02)条,其中血管直径为(300.00±119.83) μm,血管形态不一,软件计算时对于微动脉与微静脉的辨认则比较困难。 在血管造影摄片组中,膝关节周围可见数支微血管显影,其中长度超过1mm并可计数的血管数为(14.12± 1.47)条,计数的血管直径平均为(608.33±274.62) μm (图1B)。微血管网自股动脉分出后成爪牙状分布于膝关节周围软组织中,有一两支细小分支营养股骨远端和胫骨平台,最大分支向远端续于胫后动脉。 在CT扫描重建组中,在膝关节后方可见膝部的动脉发出数支细小分支,环绕膝关节周围,并营养周围肌肉组织和骨组织,可计数的微血管数为(9.00±1.79)条,平均直径为(905.00±174.56) μm,部分微血管显影不完整或不清晰,计数相对困难(图1C)。"
| [1]He X, Dziak R, Yuan X, et al. BMP2 genetically engineered MSCs and EPCs promote vascularized bone regeneration in rat critical-sized calvarial bone defects. PLoS One. 2013;8(4): e60473. PMID:23565253 [2]Carano RA, Filvaroff EH. Angiogenesis and bone repair. Drug Discov Today. 2003;8 (21):980-989.[3]Kanczler JM, Oreffo RO. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis: the potential for engineering bone. Eur Cell Mater. 2008;15:100- 114.[4]曾启龙,牡丹,施健.不同模式减影血管造影遥控对比剂跟踪技术应用[J]. 浙江临床医学,2010,12(5):461-463.[5]李洁羽,叶韵斌,陈淑萍,等.三种标记法对脐血CD34^+造血干细胞绝对计数的比较分析[J].中华检验医学杂志,2007,30(3): 348-350.[6]Westerlaan HE, van Dijk JM, Jansen-van der Weide MC, et al. Intracranial aneurysms in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: CT angiography as a primary examination tool for diagnosis--systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology. 2011;258(1):134-145. [7]McKinney AM, Palmer CS, Truwit CL, et al. Detection of aneurysms by 64-section multidetector CT angiography in patients acutely suspected of having an intracranial aneurysm and comparison with digital subtraction and 3D rotational angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 ; 29(3):594-602. [8]Iyyampillai G, Raman ET, Rajan DV, et al. Determinants of Femoral Tunnel Length in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: CT Analysis of the Influence of Tunnel Orientation on the Length. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013; 25(4):207-214.[9]Walsh DA, McWilliams DF, Turley M J, et al. Angiogenesis and nerve growth factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(10):1852-1861.[10]Ellabban AS, Kamel SR, Ahmed SS, et al. Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand serum and synovial fluid level. A comparative study between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatollnt. 2012;32(6):1589-1596.[11]李涛,崔惠勤. 膝关节髌下脂肪垫区滑膜病变的MRI诊断[J]. 影像诊断与介入放射学,2012,21(3):201-204.[12]李锐,郭燕丽. 类风湿性关系炎膝关节滑膜及血管增殖的高频超声研究[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志,2000,9(9):53-555.[13]王簕,裴国献,高梁斌,等. 血管化组织工程骨修复兔股骨干骨缺损[J]. 中华医学杂志,2010,90(23):1637-1641. [14]Wang L, Fan H, Zhang ZY, et al. Osteogenesis and angiogenesis of tissue-engineered bone constructed by prevascularized β-tricalcium phosphate scaffold and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(36): 9452-9461.[15]Kneser U, Schaefer DJ, Polykandriotis E,et al. Tissue engineering of bone: the reconstructive surgeon's point of view. J Cell Mol Med. 2006;10(1):7-19.[16]Zhou J, Lin H, Fang T,et al. The repair of large segmental bone defects in the rabbit with vascularized tissue engineered bone. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6):1171-1179. [17]Tsigkou O, Pomerantseva I, Spencer JA, et al. Engineered vascularized bone grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(8):3311-3316. [18]Buschmann J, Welti M, Hemmi S, et al. Three-dimensional co-cultures of osteoblasts and endothelial cells in DegraPol foam: histological and high-field magnetic resonance imaging analyses of pre-engineered capillary networks in bone grafts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(3-4):291-299.[19]赵震宇,邵林,刘建宇,等.新型外固定器制作大鼠负重骨节段性骨缺损模型的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(12): 1160-1163. [20]张余,尹庆水,徐国洲,等.复合珊瑚羟基磷灰石人工骨异位成骨效应的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2002,18(5):458-461.[21]谢能峰,苏伟,李尚政,等.膝后主要血管神经束的MRI定位及临床意义[J].广东医学,2013,34(9):1359-1361.[22]赵绵松,夏蓉晖,王玉华,等.骨关节炎与类风湿关节炎患者膝关节滑膜中血管内皮生长因子及血管形态的特征[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2012,44(6):927-931.[23]邹仲之.组织学与胚胎学[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2001: 107.[24]Zou D, Zhang Z, He J, et al. Blood vessel formation in the tissue-engineered bone with the constitutively active form of HIF-1α mediated BMSCs. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7): 2097- 2108. [25]Beier JP, Hess A, Loew J, et al. De novo generation of an axially vascularized processed bovine cancellous-bone substitute in the sheep arteriovenous-loop model. Eur Surg Res. 2011;46(3):148-155. [26]Cedola A, Campi G, Pelliccia D,et al. Three dimensional visualization of engineered bone and soft tissue by combined x-ray micro-diffraction and phase contrast tomography. Phys Med Biol. 2014;59(1):189-201. [27]Liu FY, Wang MQ, Fan QS, et al. Clinical application of the three-dimensional CT of the flat-panel digital subtraction angiography system. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009; 29(2):298-300.[28]Lu L, Zhang LJ, Poon CS, et al. Digital subtraction CT angiography for detection of intracranial aneurysms: comparison with three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography. Radiology. 2012;262(2):605-612.[29]Götz W, Reichert C, Canullo L, et al. Coupling of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in bone substitute healing - a brief overview. Ann Anat. 2012;194(2):171-173.[30]Pal A, Clarke JM, Cameron AE. Case series and literature review: popliteal artery injury following total knee replacement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(6):430-435. [31]解先宽,李杭,郑强,等. 膝关节周围骨折、脱位伴血管损伤的诊疗分析[J]. 中华外科杂志,2009,47(23):1794-1797.[32]Lewis RA. Medical phase contrast x-ray imaging: current status and future prospects. Phys Med Biol. 2004;49(16): 3573-3583.[33]Matsuki M, Kani H, Tatsugami F, et al. Preoperative assessment of vascular anatomy around the stomach by 3D imaging using MDCT before laparoscopy-assisted gastrectomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183(1):145-151. [34]Miyaki A, Imamura K, Kobayashi R, et al. Preoperative assessment of perigastric vascular anatomy by multidetector computed tomography angiogram for laparoscopy-assisted gastrectomy. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2012;397(6):945-950.[35]范猛,汪爱媛,王玉,等. 基于Micro-CT的骨内微血管显影和三维重建[J]. 南开大学学报:自然科学版,2011,44(1):78-84.[36]Patel PA, Chen W, Wilkening MW, et al. Extended composite temporoparietal fascial flap: clinical implications for tissue engineering in mandibular reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24(1):273-277. [37]Scala M, Gipponi M, Pasetti S, et al. Clinical applications of autologous cryoplatelet gel for the reconstruction of the maxillary sinus. A new approach for the treatment of chronic oro-sinusal fistula. In Vivo. 2000;21(3):541-547. [38]王健明,孙富广,朱文彬,等. 64层螺旋CT血管成像及三维重建后处理技术对活体供肾血管的评估[J]. 中华移植杂志(电子版), 2013,7(2):6-9.[39]李雪萍,刘彪,黄波,等. 16层螺旋CT肺血管造影及三维重建技术在肺癌血供诊断中的价值[J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复,2013, 14(5): 495-497.[40]李国策,王志铭,雷振,等.正常犬肺动脉三维CT重建中不同剂量对比剂的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(4): 671-674.[41]谷建伟,张丽,陈志强,等.基于投影的CT图像金属伪影非线性权重校正[J].清华大学学报:自然科学版,2006,46(6):825-828.[42]陈利帮,陈春.腰椎椎弓根螺钉双皮质固定的椎前大血管三维重建的解剖学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2013,31(5):528-535.[43]刘军伟,位思荣,侯鲁强,等.旋转三维数字减影血管成像在腹部介入治疗中的应用[J].实用医药杂志,2013,30(8):707-707.[44]余元新,梁长虹,张忠林,等.多层螺旋CT肾动脉成像的图像后处理技术及临床应用[J].影像诊断与介入放射学,2005,14(2): 96-98.[45]赵宏亮,石明国,宦怡,等.先心病双源CT血管造影前瞻性序列扫描与大螺距扫描的对照研究[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2013,33(5):555-558.[46]Katzberg RW, Newhouse JH. Intravenous contrast medium-in-duced nephrotoxicity: is the medical risk really as great as we have come to believe? Radiology. 2010; 256(1): 21-28.[47]Hunsaker AR, Oliva IB, Cai T, et al. Contrast opacification using a reduced volume of iodinated contrast material and low peak kilo- voltage in pulmonary CT angiography: Objective and subjective e- valuation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195(2):118-124.[48]陈志刚,任志霞,祁永爱. 下肢动脉硬化闭塞症30例三维动态增强磁共振血管造影回顾性分析[J]. 山西医药杂志:下半月,2013, 42(11):1248-1249.[49]Chen M, Huo Y, Liu Z, et al. 192Ir endovascular irradiation prevents restenosis after balloon angioplasty in rabbit. Chin Med J (Engl). 2001;114(1):62-63.[50]罗明月,单鸿,姜在波,等.多层螺旋CT及重建技术对气管主支气管肿瘤的诊断[J].中华放射学杂志,2003,37(12):1156-1160.[51]Morales Pinzón A, Orkisz M, Rodríguez Useche CM, et al. A Semi-Automatic Method to Extract Canal Pathways in 3D Micro-CT Images of Octocorals. PLoS One. 2014;9(1): e85557.[52]Kim JG, Park SE, Lee SY. X-ray strain tensor imaging: FEM simulation and experiments with a micro-CT. J Xray Sci Technol. 2014;22(1):63-75.[53]Finelle G, Papadimitriou DE, Souza AB, et al. Peri-implant soft tissue and marginal bone adaptation on implant with non-matching healing abutments: micro-CT analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014 Jan 23.[54]Young S, Kretlow JD, Nguyen C, et al. Microcomputed tomography characterization of neovascularization in bone tissue engineeringapplications. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2008; 14(3):295-306.[55]Fei J, Peyrin F, Malaval L, et al. Imaging and quantitative assessment of long bone vascularization in the adult rat using microcomputed tomography. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010; 293(2): 215-224. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [3] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [5] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [6] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [7] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [8] | Wang Weigang, Yang Zhidong, Feng Zongquan, Wang Ding. A mid-term clinical follow-up of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with fixed bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 368-373. |
| [9] | Wang Xiaofei, Teng Xueren, Cong Linyan, Zhou Xu, Ma Zhenhua. Herbert screw internal fixation for treating adult osteochondritis dissecans of the knees [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 397-402. |
| [10] | Cheng Chongjie, Yan Yan, Zhang Qidong, Guo Wanshou. Diagnostic value and accuracy of D-dimer in periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3921-3928. |
| [11] | Wang Dasai, Zhang Yang, Cheng Yin, Wang Qiang. Efficacy and safety of staged versus simultaneous unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3929-3936. |
| [12] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| [13] | Yu Yinghao, Zhao Jijun, Liu Dongcheng, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Clinical significance of preoperative planning assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with digital imaging system for fixed-bearing prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3324-3331. |
| [14] | Deng Zhibo, Li Zhi, Wu Yahong, Mu Yuan, Mu Yuexi, Yin Liangjun. Local infiltration anesthesia versus femoral nerve block for pain control and safety after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3401-3408. |
| [15] | Dong Liping, Luo Huaiqing, Yuan Heng, Long Juan, Xu Shaohui. Effect of aging on collateral vessel growth in rats with ischemic hind limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3156-3161. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||